Varroa mite
Help slow the spread
Varroa mite (Varroa destructor) is now classified as category 2 restricted matter. It remains notifiable and all beekeepers must report, control or contain the pest.
Help slow the spread of varroa mite in Queensland:
- Monitor your hives every month.
- Report hive checks using the Bee 123 form.
- Come clean go clean, especially between apiaries.
- Use the varroa mite surveillance map to inform your decision.
Adult female varroa mite
© Queensland Government

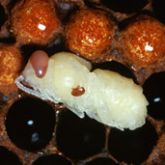
Varroa mite on pupae
© Queensland Government

Varroa mite close-up
© US Department of Agriculture Creative Commons
There are 2 species of varroa mite: Varroa destructor and Varroa jacobsoni.
- Varroa destructor remains a notifiable pest now that it is classified as restricted matter category 2.
- You can notify an authorised officer using the existing Bee123 form.
- To manage varroa mite, it is recommended to treat the pest using an integrated pest management regime.
- All states and territories are aligning to the national approach of managing varroa mite.
- Varroa jacobsoni is listed as prohibited matter under the Biosecurity Act 2014.
- This species has a wide distribution on Asian honey bee throughout Asia.
- It was detected in Townsville and at the Port of Brisbane in Queensland; however, the pest did not establish.
Scientific name
Other names
- Varroa, bee mite
Description
- Curved, pinhead-sized mite.
- Adult females are reddish-brown, flattened, oval-shaped with body 1–1.7mm long and 1.5–1.99mm wide.
- Adult males are yellowish, spherical, with body 0.75–0.98mm long and 0.70–0.88mm wide.
- May be seen on the thorax or nestled into abdominal folds of adult bees.
- Obligate parasites of honey bees and do not survive for long off a host.
To the casual observer, V. destructor and V. jacobsoni look almost identical. However, there are slight differences in size and shape between the 2 species. There are also genetic differences that enable diagnostic identification.
Habitat
- Live wherever bee colonies are found.
- Asian honey bees (Apis cerana) have adapted to withstand varroa mite infestations and are their natural host.
Distribution
Varroa mite has been found in much of Asia, Europe, the USA, South America and New Zealand.
V. destructor has been detected in Queensland. The varroa mite surveillance map displays the locations where beekeepers and government officers have reported varroa mite populations. We are working with industry to slow the spread of this species.
V. jacobsoni do not normally reproduce on European honey bees. However, they have been observed reproducing on European honey bees at some overseas locations. In Queensland, there has been no evidence to suggest V. jacobsoni has reproduced on European honey bee broods.
The movement of any of the following carriers could spread varroa mite across the country:
- bee
- swarm
- nest or hive of bees
- apiary appliance
- apiary product
- person (especially in their hair) or their personal protective equipment (e.g. bee hats, veils, suits, jackets).
Affected animals
- Asian honey bee (Apis cerana)
- European honey bee (Apis mellifera)
Impacts
Environmental
Varroa mite numbers build up over time, eventually killing honey bee nests and hives if appropriate management strategies are not applied.
Varroa mite can cause:
- scattered brood
- crippled and crawling honey bees
- impaired flight performance
- a lower rate of return to the colony after foraging
- a reduced lifespan
- significantly reduced weight of worker bees.
Colony symptoms, commonly called parasitic mite syndrome, include:
- abnormal brood pattern
- sunken and chewed cappings
- larvae slumped in the bottom or side of the cell.
This ultimately causes a reduction in managed and feral honey bee populations, supersedure of queen bees, and eventual colony breakdown and death.
Varroa mite can carry bee viruses, including exotic viruses like deformed wing virus. These viruses can be more devastating to bee colonies than the mite themselves.
Economic
- Potential to severely affect honey production.
- Potential to severely affect a wide range of pollination-reliant food crops and crops that support primary food production like:
- apples
- pears
- berries
- mangoes
- avocados
- cotton
- macadamia.
Control
Slowing the spread of varroa mite (V. destructor) in Queensland will give industry time to learn and adopt the best ways to manage the pest.
Early detection is essential to manage varroa mite populations at appropriate mite threshold levels.
Management
- Monitor hives every month using the alcohol wash method and report the results using the Bee 123 form, even if no mites are found.
- Immediately report:
- unexpected hive deaths
- deformed bees
- bees with parasites
- poor brood patterns
- dead brood.
- Approved agricultural chemicals are available for use once mite threshold levels are met. Chemicals should only be applied on a rotational basis in an integrated pest management regime.
- Find out more about managing varroa mite or email varroa@dpi.qld.gov.au.
Legal requirements
Everyone in Queensland has a general biosecurity obligation (GBO) under the Biosecurity Act 2014 (the Act) to manage biosecurity risks. Under the Act, you must:
- report all detections or suspected detections of varroa mite within 24 hours using the Bee 123 form
- take all reasonable and practical steps under your control to minimise any associated risks by reducing, controlling or containing the pest.
This is especially important to protect the broader beekeeping industry and those who rely on it.
Prohibited matter
V. jacobsoni remains listed as prohibited matter under the Act.
Restricted matter
V. destructor is classified as category 2 restricted matter. You must report it to an authorised officer using Bee 123 form and reduce, control or contain the pest.
Learn more about V. destructor being classified as restricted matter.
Actions for beekeepers
All beekeepers must:
- immediately report any significant changes
- come clean and leave clean and use decontamination practices between apiaries
- implement good husbandry practices to minimise the risk of spreading pests and diseases between sites
- perform regular hive inspections (monthly is recommended) and manage varroa mite populations according to mite loading
- follow current regulatory requirements when moving bees and beekeeping equipment
- move hives and apiary equipment using a direct route and in a quarantine-secure manner
- keep up-to-date records of operational activities (chemical usage, movements, hive inspections and results).
International ports
The Australian Government monitors cargo ships entering Australian ports for bees and other unwanted insect pests. If you find a swarm in an international airport or seaport, call 1800 798 636.
Further information
- Subscribe to our bee alert to stay up-to-date with the latest information.
- Bee Aware—Information for beekeepers and growers about honey bee biosecurity and pollination of agricultural and horticultural crops.
- Varroa mite transition to management—NSW Department of Primary Industries
- AHBIC varroa chemical treatment table—Australian Honey Bee Industry Council
- Apply for a Community Bee Innovation Fund grant.
- Contact us online, by phone or in person.